Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. (QIMC) Confirms Third Major Natural Hydrogen Discovery in Nova Scotia with Soil-Gas Results up to 4,125 ppm
newsfilecorp.com
September 22, 2025 7:00 AM EDT | Source: Quebec Innovative Materials Corp.
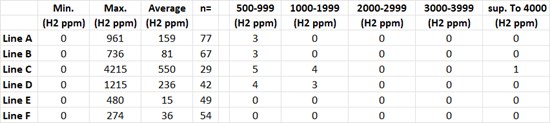
Montreal, Quebec--(Newsfile Corp. - September 22, 2025) - Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. (CSE: QIMC) (OTCQB: QIMCF) (FSE: 7FJ) ("QIMC" or the "Company") is pleased to announce the discovery of a third major clean hydrogen zone in Nova Scotia. Soil-gas surveys conducted in the Southampton and East-Southampton areas returned 23 samples above 500 parts per million (ppm) hydrogen, of which 8 exceeded 1,000 ppm, including a peak value of 4,125 ppm - one of the highest concentrations recorded by the Company in the province to date.
"The confirmation of a third hydrogen zone in Nova Scotia, with 23 samples above 500 ppm including 8 over 1,000 ppm and a peak of 4,125 ppm, represents a transformative step for QIMC. Each new anomalous zone further validates our thesis that the Cumberland Basin is one of the most promising natural hydrogen districts in North America. Importantly, geology shows deformation and folding of rocks between the features that present strong similarities with the Carboniferous Basin of Lorraine in Europe, in both cases, we are in a carboniferous basin containing continental sedimentary rocks, including coal rocks, among others. With the integration of seismic data into our exploration model, QIMC is positioned - alongside Nova Scotia - at the forefront of clean hydrogen development," said John Karagiannidis, President & CEO of QIMC.
This latest discovery zone builds on QIMC's previously announced results at West Advocate and Eastern Advocate, further confirming Nova Scotia's Cumberland Basin as one of North America's most promising emerging natural hydrogen hubs. With three major zones now confirmed, the QIMC and INRS teams are expanding our Phase 2 and Phase 3 programs in these areas.
"Following recent meetings with our partners, we are also evaluating the next phase of development, which includes the integration of ammonia production into our model, leveraging Nova Scotia's existing infrastructure and port facilities," adds John Karagiannidis.
Geological Context of Southampton
The geomorphological and geological contexts of the Southampton area are markedly different from those of the tectonized zone of the Cobequid Highlands in the Advocate and West-Advocate areas. As a result, the discovery of a new hydrogen anomalous domain in the Southampton area is noteworthy and must be interpreted in terms of geological characteristics specific to the Cumberland Carboniferous Basin.
Prof. Marc Richer-Laflèche (INRS) commented: "The Southampton anomalies highlight a structural and geological setting distinct from Advocate. Here we are working within a Carboniferous basin environment, which provides a unique context for hydrogen migration and accumulation."
Structural Controls and Basin Setting
As shown on the elevation data map (Fig. 1a), hydrogen soil-gas anomalies are located on a lower elevation plateau north of the Cobequid Highlands. This topography is influenced by a regional fault system separating the Carboniferous domains of the Cumberland Basin to the north (Pennsylvanian sedimentary rocks) from the older granitic and Neoproterozoic volcanic-sedimentary terrains of the Jeffers Group to the south (Fig. 1c).
This geological contrast is clearly expressed by a magnetic high on Nova Scotia's regional aeromagnetic map (Fig. 2). On a local scale, magnetic and gravimetric surveys show low potential field values, which encompass most of the highest hydrogen anomalies observed. Such zones typically indicate a thickening of sedimentary sequences in basins.
Seismic Data Integration
Seismic reflection data, reprocessed by the Geological Survey of Canada (Durling, 2023), underline the importance of the Athol syncline, which reaches a depth of ~5 km beneath the anomalous Southampton sector. This section also shows the presence of at least four south-dipping faults.
In QIMC's exploration model, these faults act as migration conduits, promoting the upward movement of hydrogen to surface soils (Fig. 3).
Prof. Richer-Laflèche added: "The seismic integration is critical. It shows the geometry of the basin, the depth of the Athol syncline, and the role of fault systems that facilitate hydrogen migration. This structural picture strengthens our confidence in the Southampton anomalies."
Lithological Associations
The highest hydrogen concentrations were observed over the Carboniferous Ragged Reef Formation, composed of alternating fluvial sandstones, conglomerates, mudstones, lacustrine limestones, and rare coal horizons. In contrast, soils overlying the Malagash Formation did not display hydrogen anomalies.
Structurally, the strongest anomalies coincide with zones affected by secondary south-dipping faults trending EW to WNW-ESE. These features appear to intersect a subvertical strike-slip fault along the southern margin of the Cumberland Basin, at the foot of the Cobequid Uplands.
Conceptually, this geological and structural framework suggests hydrogen formation result from groundwater infiltration into south-dipping faults and reactions at depth with igneous rocks of the Cobequid Highlands. The well-documented high geothermal gradient of the Cumberland Basin acts as a catalyst for such hydrogen-producing processes.
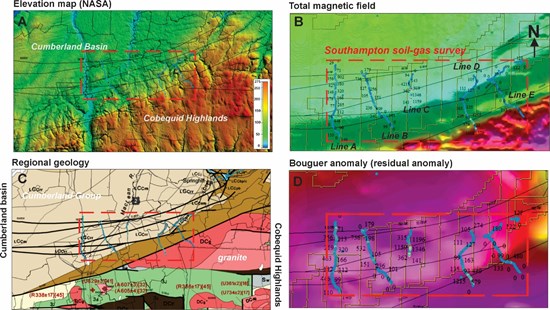
Figure 1. A) NASA elevation map (in m), B) total magnetic field map, C) simplified geological map D) residual Bouguer anomaly (gravimetry). Maps from the novascotia.ca site. The red box shows the perimeter of the Soil-Gas survey conducted in the Southampton and East-Southampton areas.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
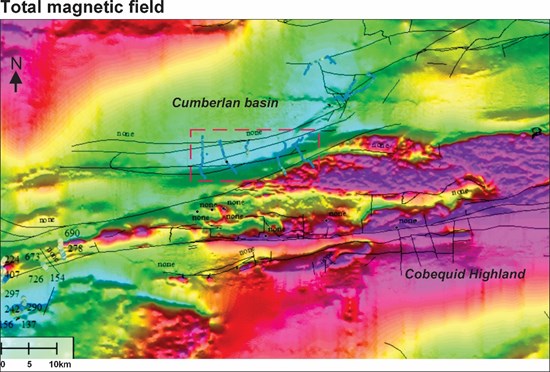
Figure 2. Map of the total magnetic field of part of the Cumberland Basin and the Cobequid Highlands. Map from the novascotia.ca site. The red box shows the perimeter of the Soil-Gas survey conducted in the Southampton and East-Southampton areas.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
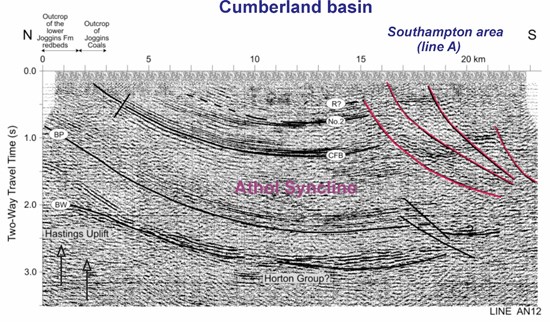
Figure 3. AN12 seismic reflection line reprocessed by the Geological Survey of Canada (Durling, 2023). The faults shown in red (Southampton area) are those observed within the perimeter of the Soil-Gas surveys conducted in Southampton.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
Analytical results from the Soil-Gas surveys in the Southampton and East-Southampton areas.
The work was carried out from 2 to 11 August 2025, under sunny weather conditions that were particularly favourable for the collection of Soil-Gas samples (average temperature of 29.9oC, average atmospheric pressure of 1047 HPa and average relative humidity of 35.9%). A total of 318 samples were collected from 6 sections totalizing 28.6 km along public roads of Southampton and East-Southampton.
The mean and median hydrogen concentrations measured in the soils of this sector are particularly variable. Minimum, maximum and average concentrations are presented in table 1. The sections of the Soil-Gas surveys are presented in Figure 4 and the spatial distribution map of the hydrogen anomalies is presented in Figure 5.
Prof. Richer-Laflèche concluded: "The Southampton results, with values up to 4,215 ppm, align with our exploration model and underscore the potential of the Cumberland Basin to host multiple hydrogen-rich domains."
Table 1: H2 soil-gas geochemistry in Southampton and East-Southampton public roads
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
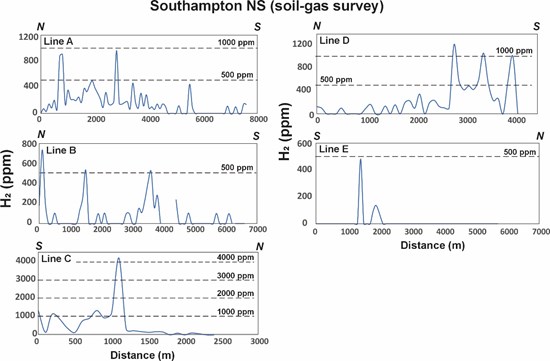
Figure 4. Results of the Soil-Gas survey for hydrogen in the Southampton and East-Southampton areas.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
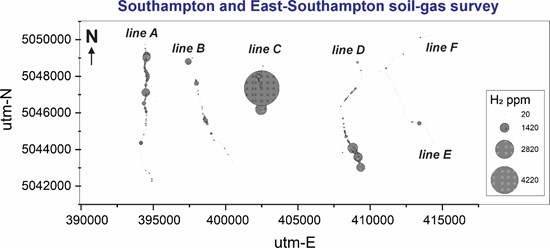
Figure 5. Map of the spatial distribution of hydrogen analysis results in soils from the Southampton and East-Southampton sectors.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
images.newsfilecorp.com
About Pr. Marc Richer-LaFlèche, P.Geo.
Pr. Richer-Laflèche, a qualified expert in hydrogen exploration, has reviewed, read and approved the technical content presented in this press release. Pr. Richer-Laflèche confirms that the methodologies employed, data presented, and interpretations made conform to current industry practices and standards relating to hydrogen exploration.
About QIMC
Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. is a mineral exploration and development company dedicated to exploring and harnessing the potential of North America's abundant resources. With properties in Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia and Minnesota (US), QIMC is focused on specializing in the exploration of white (natural) hydrogen and high-grade silica deposits. QIMC is committed to sustainable practices and innovation. With a focus on environmental stewardship and cutting-edge extraction technology, we aim to unlock the full potential of these materials to drive forward clean energy solutions to power the AI and carbon-neutral economy and contribute to a more sustainable future.
QUÉBEC INNOVATIVE MATERIALS CORP.
John Karagiannidis
Chief Executive Officer
For further information, please contact:
Email: info@qimaterials.com
Tel: +1 514-726-7058
Reference:
Durling, P. 2023. Seismic-reflection interpretation of the carboniferous Cumberland Basin, northern Nova Scotia. Geological Survey of Canada Open File 2816-7155; 8937. 64 pages.
Neither the Canadian Securities Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the CSE policies) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release and has neither approved nor disapproved the contents of this news release.
Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains statements that constitute "forward-looking statements". Such forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause Québec Innovative Materials' actual results, performance or achievements, or developments in the industry to differ materially from the anticipated results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts and are generally, but not always, identified by the words "expects," "plans," "anticipates," "believes," "intends," "estimates," "projects," "potential" and similar expressions, or that events or conditions "will," "would," "may," "could" or "should" occur.
Although Québec Innovative Materials believes the forward-looking information contained in this news release is reasonable based on information available on the date hereof, by their nature, forward-looking statements involve assumptions, known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause our actual results, performance or achievements, or other future events, to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements.
Examples of such assumptions, risks and uncertainties include, without limitation, assumptions, risks and uncertainties associated with general economic conditions in Canada and abroad; adverse industry events; future legislative and regulatory developments in the natural resources sector, in particular as regards the regulation of white (natural) hydrogen exploration, development and exploitation; the Company's ability to access sufficient capital from internal and external sources, and/or inability to access sufficient capital on favorable terms; natural resources industry and markets in Canada and generally; the ability of Québec Innovative Materials to implement its business strategies; competition; and other assumptions, risks and uncertainties.
The forward-looking information contained in this news release represents the expectations of the Company as of the date of this news release and, accordingly, is subject to change after such date. Readers should not place undue importance on forward-looking information and should not rely upon this information as of any other date. While the Company may elect to, it does not undertake to update this information at any particular time except as required in accordance with applicable laws.
Cautionary Statements This news release contains "forward-looking information" and "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of applicable Canadian securities legislation. These statements are based on expectations, estimates, and projections as of the date of this release. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, which may cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these statements, as no assurance can be provided regarding future outcomes.
 SOURCE: Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. SOURCE: Quebec Innovative Materials Corp. |










