Distributed
Australia adds 2 GWh of home battery storage in less than four months
In less than four months since 1 July 2025, the Australian government’s Cheaper Home Batteries program has directly increased home battery capacity across the country by more than 50% and delivered 2 GWh of battery storage through 100,000 installations.

By
Ev Foley
Oct 27, 2025
Distributed
Projects & Applications

Image: Sonnen
In less than four months since 1 July 2025, the Australian government’s Cheaper Home Batteries (CHB) program has directly increased home battery capacity across the country by more than 50% and delivered 2 GWh of battery storage through 100,000 installations.
The $2.3 billion (USD 1.5 billion) program is designed to stimulate a home-battery installation catch up to the 4,216,229 rooftop solar installations nationwide (as of 15 October 2025), which according to the Clean Energy Regulator’s (CERs) small-scale installation postcode data, have a rated output of 27,326,449 kW and represent 26.8 GW of clean power.
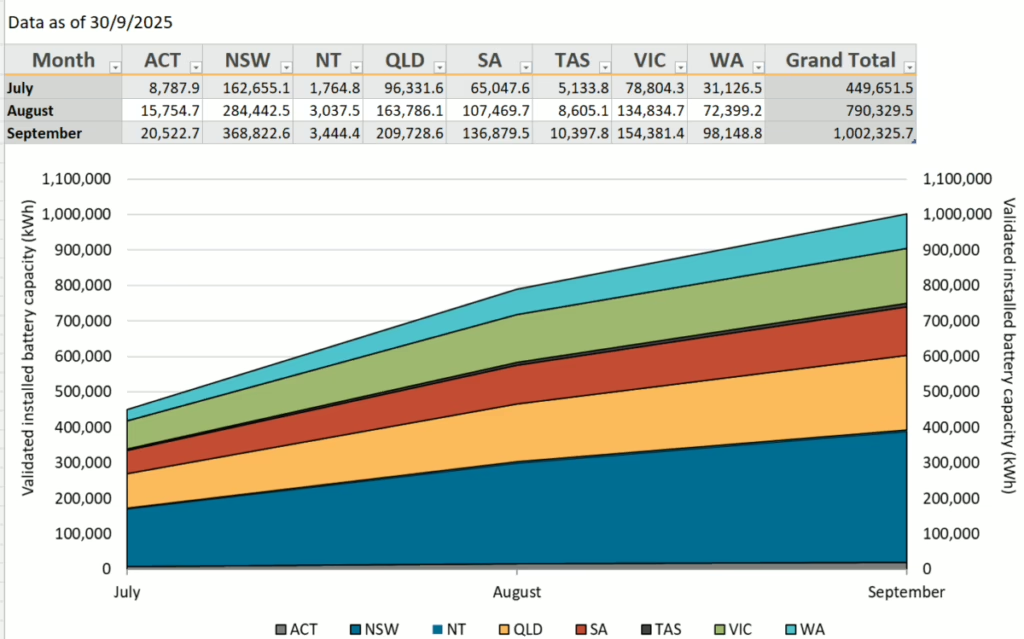
Small-scale cumulative validated battery capacity installed by state and territory in kWh, representing small-scale technology certificates received in the previous 12-months to 30 September 2025.Image: Clean Energy Regulator The CHB offers an approximate 30% discount on upfront costs to install small-scale battery systems (5 kWh to 100 kWh).
CER’s data shows to 30 September 2025 the majority (14,297) of battery installations since 1 July 2025 have 15-20 kWh capacity, followed by 13,358 10-15 kWh batteries, while just 307 in the three month period were in the 50-100 kWh capacity range, based on small-scale technology certificates received to date.
Federal Minister for Climate Change and Energy Chris Bowen said Australia is a solar nation – with the highest rate of rooftop solar anywhere in the world.
“Our program takes the next step, delivering a game changer for household bills. In just four months, 100,000 Aussie families have jumped at the opportunity to slash their energy bills for good by installing a Cheaper Home Battery,” Bowen said.
Vehicle-to-grid chargers On the back of the CHB program, the Electric Vehicle Council (EVC) advocate for a $3,000 rebate to be included in the CBH for 50,000 vehicle-to-grid (V2G) chargers in by the end of 2028, at a cost of $150 million.
EVC Chief Executive Officer Julie Delvecchio said V2G has potential to stabilise the grid.
“EVs can store up to five times more energy than a typical home battery. That a huge untapped resource sitting in driveways and with the right technology, we can use it to save money and support the grid, and make the whole system more reliable for everyone,” Delvecchio said.
“V2G enables EV owners to feed stored power back into the grid during periods of high demand, when electricity is most expensive and vulnerable to disruptions like blackouts.
From pv magazine Australi
ess-news.com |







