Goddard is a liar. Given the number of his lies that you post, so are you.
Arctic sea ice reaches lowest maximum extent on record
March 19, 2015
On February 25, 2015, Arctic sea ice extent appeared to have reached its annual maximum extent, marking the beginning of the sea ice melt season. This year’s maximum extent not only occurred early; it is also the lowest in the satellite record. However, a late season surge in ice growth is still possible. NSIDC will post a detailed analysis of the 2014 to 2015 winter sea ice conditions in early April.
Overview of conditions
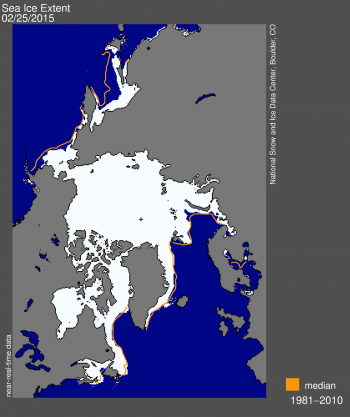 Figure 1. Arctic sea ice extent for February 25, 2015 was 14.54 million square kilometers (5.61 million square miles). The orange line shows the 1981 to 2010 median extent for that day. The black cross indicates the geographic North Pole. Sea Ice Index data. About the data Figure 1. Arctic sea ice extent for February 25, 2015 was 14.54 million square kilometers (5.61 million square miles). The orange line shows the 1981 to 2010 median extent for that day. The black cross indicates the geographic North Pole. Sea Ice Index data. About the data
Credit: National Snow and Ice Data Center
High-resolution image
On February 25, 2015 Arctic sea ice likely reached its maximum extent for the year, at 14.54 million square kilometers (5.61 million square miles). This year’s maximum ice extent was the lowest in the satellite record, with below-average ice conditions everywhere except in the Labrador Sea and Davis Strait. The maximum extent is 1.10 million square kilometers (425,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average of 15.64 million square kilometers (6.04 million square miles) and 130,000 square kilometers (50,200 square miles) below the previous lowest maximum that occurred in 2011. This year’s maximum occurred 15 days earlier than the 1981 to 2010 average date of March 12. The date of the maximum has varied considerably over the years, occurring as early as February 24 in 1996 and as late as April 2 in 2010.
Because of the variability of ice extent at this time of year, there can be some delay in pinpointing the date of the maximum extent, as was true this year. NSIDC calculates daily ice extent as an average of the previous five days (see the Sea Ice Index documentationfor more information), and we also look for a clear downward trend for a number of days.
While the downturn in extent was quite pronounced on February 25, the trend subsequently flattened. This is in part due to recent ice growth in the Bering Sea, partly balancing continued ice retreat in the Barents and Kara seas. Over the next two to three weeks, periods of increase are still possible. However, it now appears unlikely that there could be sufficient growth to surpass the extent reached on February 25.
Conditions in context
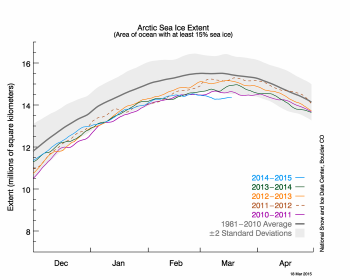 Figure 2. The graph above shows Arctic sea ice extent as of March 18, 2015, along with daily ice extent data for four previous years. 2014 to 2015 is shown in blue, 2013 to 2014 in green, 2012 to 2013 in orange, 2011 to 2012 in brown, and 2010 to 2011 in purple. The 1981 to 2010 average is in dark gray. The gray area around the average line shows the two standard deviation range of the data. Sea Ice Index data. Figure 2. The graph above shows Arctic sea ice extent as of March 18, 2015, along with daily ice extent data for four previous years. 2014 to 2015 is shown in blue, 2013 to 2014 in green, 2012 to 2013 in orange, 2011 to 2012 in brown, and 2010 to 2011 in purple. The 1981 to 2010 average is in dark gray. The gray area around the average line shows the two standard deviation range of the data. Sea Ice Index data.
Credit: National Snow and Ice Data Center
High-resolution image
Over the 2014 to 2015 winter season, sea ice extent grew 9.91 million square kilometers (3.83 million square miles). This was substantially less ice growth than last year, which saw record growth over the winter. Part of the explanation for the record low maximum lies with recent weather patterns. As discussed in our previous post, February was characterized by an unusual configuration of the jet stream, leading to warm conditions over the Pacific side of the Arctic that maintained low sea ice extent in the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk. Furthermore, since the last half of February through the middle of March, the Arctic Oscillationwas in a strongly positive phase, with index values exceeding 5.0 for several days in the first week of March. This has been expressed as a strong Icelandic Low, a semi-permanent area of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending into the Barents Sea. The strong Icelandic Low led to a pattern of surface winds over the Barents and Kara seas with an unusually strong component from the south.
Over the first two weeks of March, temperatures throughout the eastern Arctic at the 925 hPa level (approximately 3,000 feet altitude) were several degrees Celsius above average, with temperatures as much as 8 to 10 degrees Celsius (14 to 18 degrees Fahrenheit) above average in the Barents Sea between Svalbard and Franz Josef Land.
While the seven-day weather forecasts show continued warmer-than-average conditions over the eastern Arctic, colder-than-average conditions are expected over the Bering Sea and may still lead to some new ice formation. Thus, while the maximum appears to have occurred on February 25, late season ice growth may still occur.
Final analysis pendingAt the beginning of April, NSIDC scientists will release a full analysis of winter conditions, along with monthly data for March. For more information about the maximum extent and what it means, see the NSIDC Icelights post, the Arctic sea ice maximum.
nsidc.org |






