Actually it's a lot more.
When you study topographical maps it becomes pretty obvious especially when you match it with population density.
Just look at New Orleans.
Much of it below sea level.
Elevation
See also: Drainage in New Orleans
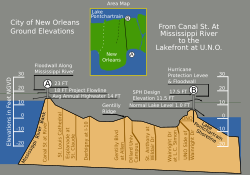
Vertical cross-section, showing maximum levee height of 23 feet (7.0 m) New Orleans was originally settled on the river's natural levees or high ground. After the Flood Control Act of 1965, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers built floodwalls and man-made levees around a much larger geographic footprint that included previous marshland and swamp. Over time, pumping of water from marshland allowed for development into lower elevation areas. Today, half of the city is at or below local mean sea level, while the other half is slightly above sea level. Evidence suggests that portions of the city may be dropping in elevation due to subsidence. [108]
A 2007 study by Tulane and Xavier University suggested that "51%... of the contiguous urbanized portions of Orleans, Jefferson, and St. Bernard parishes lie at or above sea level," with the more densely populated areas generally on higher ground. The average elevation of the city is currently between 1 and 2 feet (0.30 and 0.61 m) below sea level, with some portions of the city as high as 20 feet (6 m) at the base of the river levee in Uptown and others as low as 7 feet (2 m) below sea level in the farthest reaches of Eastern New Orleans. [109] [110] A study published by the ASCE Journal of Hydrologic Engineering in 2016, however, stated:
...most of New Orleans proper—about 65%—is at or below mean sea level, as defined by the average elevation of Lake Pontchartrain [111]
The magnitude of subsidence potentially caused by the draining of natural marsh in the New Orleans area and southeast Louisiana is a topic of debate. A study published in Geology in 2006 by an associate professor at Tulane University claims:
While erosion and wetland loss are huge problems along Louisiana's coast, the basement 30 feet (9.1 m) to 50 feet (15 m) beneath much of the Mississippi Delta has been highly stable for the past 8,000 years with negligible subsidence rates. [112]
The study noted, however, that the results did not necessarily apply to the Mississippi River Delta, nor the New Orleans metropolitan area proper. On the other hand, a report by the American Society of Civil Engineers claims that "New Orleans is subsiding (sinking)": [113]
Large portions of Orleans, St. Bernard, and Jefferson parishes are currently below sea level—and continue to sink. New Orleans is built on thousands of feet of soft sand, silt, and clay. Subsidence, or settling of the ground surface, occurs naturally due to the consolidation and oxidation of organic soils (called "marsh" in New Orleans) and local groundwater pumping. In the past, flooding and deposition of sediments from the Mississippi River counterbalanced the natural subsidence, leaving southeast Louisiana at or above sea level. However, due to major flood control structures being built upstream on the Mississippi River and levees being built around New Orleans, fresh layers of sediment are not replenishing the ground lost by subsidence. [113]
In May 2016, NASA published a study which suggested that most areas were, in fact, experiencing subsidence at a "highly variable rate" which was "generally consistent with, but somewhat higher than, previous studies." [114]
en.wikipedia.org |





