GoldHaven Resources Identifies Critical, Base and Precious Metals at Magno Project: Indium, Tin, Zinc, Silver & Gold Highlight Exploration Potential
globenewswire.com
August 14, 2025 09:00 ET | Source: GoldHaven Resources Corp.
VANCOUVER, British Columbia, Aug. 14, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- GoldHaven Resources Corp. ("GoldHaven" or the "Company") (CSE: GOH) (OTCQB: GHVNF) (FSE: 4QS) is pleased to provide an update following further studies and interpretation completed on its Magno Project (the “Project”) located in northern British Columbia (“BC”), Canada.
The Project is a district-scale polymetallic property situated in the Liard Mining Division, adjacent to the historic Cassiar mining district in Northern BC, Canada
The Company holds 100% ownership of the Magno mineral claims in British Columbia. The Project spans 30,573.53 hectares and is situated within the historically rich Liard Mining Division. The Project is accessible via Highway 37, which crosses the southeastern claim area, providing good access for future exploration and development work.
?
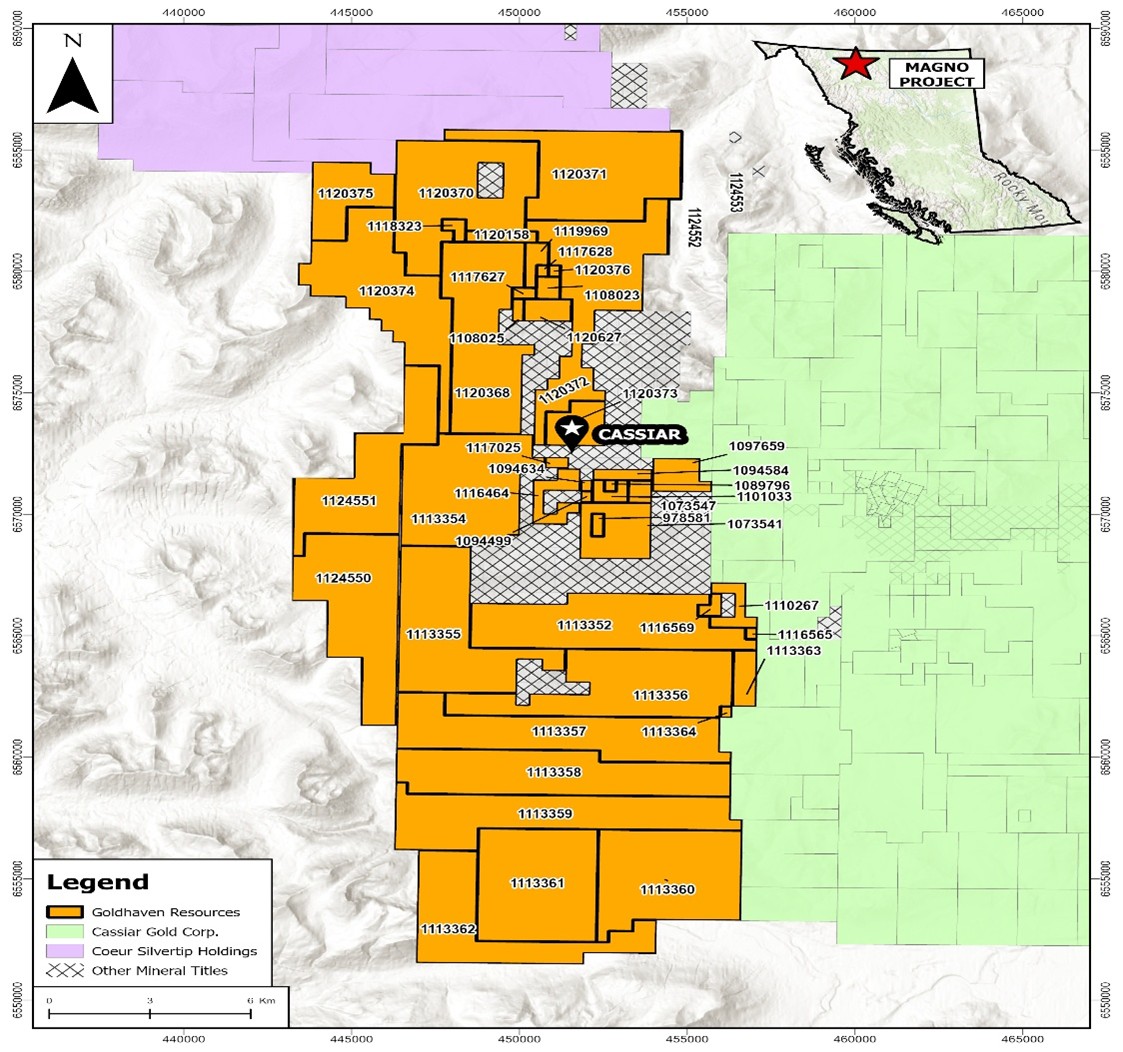
Figure 1: Magno property with BC regional geology highlighting historical work and present showings
The Magno Project hosts several critical metals, including tin (Tn), indium (In), zinc (Zn), silver (Ag) gold (Au), tungsten (W), and gallium (Ga) which are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, batteries, and green energy technologies. Additionally, the Project hosts several different styles of base metal (zinc-lead) mineralization, including skarn and carbonate replacement styles along with potential for deeper porphyry-associated copper-molybdenum-tin mineralization. GoldHaven is looking to apply new geological research to potentially overlooked areas to analyze a broad range of these critical and strategic metals to vector in on potential porphyry mineralization.
Critical Metals at Magno: A Strategic Opportunity
Data from the Magno historical workings highlight the potential for significant concentrations of technology-critical metals in addition to the established base and precious metal potential. As global industries face supply shortages of indium, tin, gallium, tungsten and strategic base metals like zinc, Magno presents an attractive opportunity in a geopolitically stable and mining-friendly jurisdiction of Canada.
The Project covers the contact zone between the mid-Cretaceous-aged Cassiar Batholith and the late Proterozoic to late Paleozoic carbonate and clastic sedimentary rocks of the Cassiar Terrane. Base metal (zinc-lead) rich skarn and carbonate replacement mineralization, often associated with significant silver values, are widespread in the region, including on the Project. Additional historical insight identified, geochemically anomalous molybdenum (Mo), ± copper (Cu), tin and tungsten values associated with Late Cretaceous intrusions, including the 7 by 30 km Cassiar or Troutline Creek stock, which intrude the Cassiar Terrane proximal to the Cassiar Batholith. The mineralized granitic intrusions may also be the source of the skarn and carbonate replacement mineralization in the intruded sedimentary sequence.
In addition to the historical Zn-Pb-Ag and Cu-Mo mineralization, reconnaissance sampling by Johnston (2024) indicates anomalous indium and additional support for tin as potential critical metal additions. Recent research published on skarn deposits in SE China (Tan, 2024) suggests that variations in the indium/zinc ratios in skarn environments may provide a vector towards the causative source intrusion(s) and possible associated Cu-Mo+/-Sn-W mineralization. Johnston took six confirmatory samples which returned indium values ranging from 1.1 to 63.8 ppm, with three of the six samples greater than 40 ppm. Additionally, a verified sample from the Kuhn showing taken in 2019 by Fundamental Resources (AR 38356) contained 85.20 ppm indium, suggesting potential of the Cassiar Terrane to yield indium mineralization. Tin and zinc values were significant ranging from 110 to 1749 ppm tin and up to 5.58% zinc in Johnston’s samples.
This research directly supports the exploration model at Magno, where high indium values in the skarns could indicate proximity to deeper, potentially undiscovered Cu-Mo porphyry bodies. This growing body of evidence reinforces the strategic significance of the Property, not only for traditional base and precious metals but also for critical metals. Gallium and germanium are additional critical metals that may be present on the property and will be a focus for future work.
This field season, GoldHaven will look to explore the skarns with detailed geochemical analysis of Ag, Zn, Sn, In, W and Ga and correlate this data to the magmatic source of mineralization in the granites. With Mo porphyries already known to be present in the region, the Company believes the potential of locating Mo-Cu porphyry mineralization on the Magno property is very high.
Tin (Sn): A Critical Metal for Electronics & Battery Storage
Tin is an essential component of electronic circuits, lithium-ion batteries, and soldering materials, with increasing demand due to the electrification of transportation and grid storage solutions.
- Magno Project Key Grades Identified:
- 5,200 ppm Sn (Middle D Zone, Eveready 2002)
- 5,199 ppm Sn (Pant N Zone, Eveready 2003)
- 2,097 ppm Sn (Magno North, Eveready 2003)
- 1,749 ppm Sn (Middle D, Johnston 2023)?
Tin, a critical metal for electronics & battery storage, is an essential component of electronic circuits, lithium-ion batteries, and soldering materials, with increasing demand due to the electrification of transportation and grid storage solutions.
In 1978, sampling by the BC Department of Mines identified anomalous tin values on the current property. Follow-up sampling of old CCS drill core by Shell Canada in 1979 returned several anomalous tin intercepts, mainly from the Middle D Zone ranging up to 6.5% Sn over 0.9 metres. The results of samples which returned greater than 1000 ppm Sn are presented in Table 2.
| Sampler | Year | Location | Sample ID | Sn (tin) | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Middle D | R-8 | 0.86%/3.0m | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Middle D | R-3 | 0.9%/0.9m | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Middle D | R-3 | 0.33%/1.2m | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Middle D | R-10 | 6.5%/0.9m | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Middle West | Hole not specified | 0.32%/4.6m | | Shell Canada | 1979 | Tremolite | H-1 | 0.2%/2.0m | | Eveready | 2003 | Magno North | 7875 | 1940 ppm | | Eveready | 2003 | Magno North | 7878 | 2097 ppm | | Eveready | 2002 | Middle D | 7700 | 5200 ppm | | Eveready | 2003 | Pant North | 7854 | 5199 ppm | | Johnston | 2023 | Middle D | 725610 | 1749 ppm |
Table 1: Anomalous Tin Results from the Magno Property (see Magno 43-101 filed on SEDAR+)
*This work was carried out prior to the introduction of NI 43-101 and the results have not been verified by a Qualified Person, except for the samplings by Johnston and Eveready, and hence cannot be relied upon. However, the company believes the results presented suggest the possibility of previously unrecognized tin mineralization on the property. Verifying this potential will be one of the objectives of the 2025 summer work program.
Indium (In): A High-Tech & Green Energy Essential
Indium is a critical metal for semiconductors, solar panels and LCD displays primarily recovered as a byproduct of zinc mining and smelting. Reconnaissance sampling on the Magno Project combined with recent confirmatory sampling by Johnston, a Qualified Person, suggests potential for significant quantities of indium associated with the known zinc mineralization. Three of six samples collected by Johnston from the Magno Project for confirmation returned indium values exceeding 40 ppm In, all ranging from 1.2 to 63.8 ppm In.
Indium is indispensable to modern technology, as it is a key component of indium-tin oxide (ITO), the transparent conducting film used in virtually all flat-panel displays and touchscreens. Its unique combination of transparency, electrical conductivity, and strong adherence to glass makes it irreplaceable for applications in smartphones, tablets, televisions, and high-tech architectural glass coatings. With 65% of global indium consumption driven by electronic displays, demand continues to rise.
Recognizing its strategic importance, indium is included on the Canadian Geological Survey’s list of 34 critical minerals. The United States is entirely reliant on imports to meet its indium demand, consuming 170 metric tons in 2018 from sources such as China (27%), Canada (22%), South Korea (11%), and Taiwan (10%).
Zinc (Zn): A Base Metal with Green Energy Potential
Zinc is an essential industrial metal, used in galvanisation, batteries and green energy technologies. The Magno Property hosts widespread zinc mineralization with associated lead and silver values in several different geological settings.
- Magno Project Key Grades Identified:
- 41% Zn (Magno South, Eveready 2004)
- 6.2% Zn, 28.2% Pb, 820 g/t Ag over 1.2m (Magno North, Eveready 2003)
- 16% Zn, 1.3% Pb, 19.3 g/t Ag, 0.9 g/t Au over 4.3m (Magno North, Eveready 2003)
- 7.4% Zn, 14.2% Pb, 398 g/t Ag (Upper D Zone, Eveready 2002)
Historic work from at least the 1960s onwards has mainly focussed on the zinc-lead-silver potential of the known carbonate replacement deposits, particularly the Middle D and Magno deposits.
Several historic reserves/resources have been defined, but since all pre-date the introduction of NI 43-101 and the work was not carried out under the supervision of a Qualified Person, these results cannot be relied upon. They do however provide a starting point for new exploration using updated geological knowledge, improved deposit models and modern geophysical and geochemical techniques and interpretations. Limited recent sampling carried out by Johnston, who is a Qualified Person, confirmed the widespread nature of zinc mineralization on the property. Of the six samples he collected, four exceeded 0.5% Zn with a maximum of 5.58% Zn.
Silver (Ag): Indispensable Metal in Modern Industry
Silver continues to play a critical role across a wide range of industrial applications. Today, it is essential in the production of solder and brazing alloys, batteries, dental materials, glass coatings, LED chips, medical devices, nuclear technology, photography, solar (photovoltaic) energy, RFID chips used for global shipment tracking, semiconductors, touch screens, water purification systems, wood preservatives, and numerous other technologies.
The Washington-based Silver Institute aptly refers to silver as “the indispensable metal,” highlighting its widespread utility.
Over the past decade, leading industrial consumers of silver have included the United States, Canada, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Germany, and Russia. While demand from traditional sectors has declined, it has been offset by increasing use in emerging and advanced technologies, underscoring silver’s enduring importance in the global economy.
The Magno Property continues to exhibit strong potential for high-grade silver, along with associated lead and zinc within replacement skarn systems, historical exploration targets that, despite their promise, were never advanced into a NI 43-101 compliant resource. Recent sampling has confirmed significant silver grades which reinforce the high-grade nature typical of this deposit style. While these results are compelling, they represent only one aspect of a broader geological picture. GoldHaven’s exploration strategy remains focused on a larger-scale opportunity, using these mineralized showings and newly collected data to guide the search for a potential buried porphyry system within the region.
| Type | Source | Year | Sample_ID | Ag ppm | Au ppb | Pb ppm | Zn ppm | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7664 | 2280 | 535 | 630000 | 6500 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7880 | 2220 | 1360 | 740000 | 4684 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7836 | 1640 | 1150 | 440000 | 18500 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7870 | 1500 | 525 | 596000 | 7644 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7868 | 1460 | 475 | 381000 | 36500 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7839 | 1340 | 730 | 535000 | 32500 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7844 | 1340 | 1550 | 445000 | 5208 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7869 | 820 | 240 | 282000 | 61900 |
Table 2 - Top Silver samples from the 2002-2003 Eveready projects (AR2720 & AR7337 J. Pautler)
| Type | Source | Year | Sample_ID | Zn ppm | Ag ppm | Au ppm | Pb ppm | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7877 | 263000 | 12.50 | 60 | 21100 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7875 | 210000 | 15.30 | 2540 | 13700 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7693 | 195000 | 208.00 | 475 | 1566 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7873 | 193000 | 176.00 | 235 | 2188 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7882 | 164000 | 76.80 | 1230 | 17800 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7691 | 109000 | 43.50 | 85 | 2764 | | Rock | AR27203 | 2002 | 7662 | 74000 | 398.00 | 890 | 142000 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7884 | 69800 | 352.00 | 625 | 87600 | | Rock | AR27337 | 2003 | 7871 | 67400 | 470.00 | 545 | 176000 |
Table 3 - Top Zinc samples from the 2002-2003 Eveready projects (AR2720 & AR7337 J. Pautler)
Tungsten (W): Resurgence as Prime Military Metal
Tungsten has emerged as a critical mineral of strategic importance due to its unmatched physical properties and indispensable role in high-performance applications. With the highest melting point of any metal and exceptional density and hardness, tungsten is essential to modern defense systems, including armor-piercing munitions, kinetic energy penetrators, and aircraft turbine components. Its resilience to extreme temperatures and wear makes it equally vital in aerospace, advanced manufacturing, and nuclear energy. These characteristics, combined with a lack of viable substitutes, position tungsten as a cornerstone of national security and industrial competitiveness.
The Kuhn and Dead Goat showings which correlate to GoldHaven’s unverified inferred resource is reflective of Skarn replacement of tungsten, molybdenum and minor copper. This area much like the Ag, Pb, Zn replacements are situated with the Cambrian stratigraphy of the Cassiar terrane. The Atan Group limestones, marbles and calcareous sedimentary rocks character of this group provide the best lithological host for such a deposit style. Below, verified surface samples are expressive of the grades which made up the inferred resource in the area. GoldHaven will be looking into verifying these results and more in the coming weeks during the field program.
| Type | Source | Year | Sample_ID | W_ppm | Cu_ppm | Mn_ppm | Mo_ppm | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-712 | 19850 | 10 | 20900 | 1750 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-713 grab | 14850 | 20 | 17850 | 1000 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-707 grab | 8360 | 20 | 21200 | 230 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-710 | 8270 | 20 | 17250 | 260 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-708 grab | 6730 | 10 | 21900 | 140 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-709 | 6400 | 60 | 18500 | 240 | | Rock | AR31833 | 2011 | KU10-AR-7 | 6030 | 2633 | 4372 | 22 | | Rock | AR31833 | 2011 | KU10-AR-8 | 5510 | 173 | 9792 | 17 | | Rock | AR32573 | 2011 | KU11AR-711 | 5240 | 10 | 17950 | 570 |
Table 4 - Surface samples by A. Kikawka P.Geo. from Fundamental Resources 2010-2011 In the Kuhn and Dead Goat Showings
Magno Project Key Grades Identified:
- Historic drilling by Shell Canada included 17 diamond drill holes totaling 1,766 metres, confirming the presence of high-grade scheelite (CaWO4) and molybdenite (MoS2).
- Recent exploration has confirmed significant tungsten and molybdenum mineralization in metasomatic skarn lenses
- Hosts a historic resource of 409,300 tonnes at 0.48% WO3 (tungsten trioxide) and 0.134% MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide) in the Kuhn North zone
This work was completed prior to the implementation of NI 43-101 standards, and the results have not been confirmed by work conducted under the supervision of a QP. The 2025 summer work program will aim to verify this potential.
Gallium (Ga): Untapped Potential in High-Tech Metals
Gallium is a strategic metal used in fiber optics, 5G networks, and advanced semiconductors. While historical exploration did not target these elements specifically, Magno's CRD deposits may host economically significant concentrations of this critical metal. GoldHaven plans to evaluate this potential further as part of its upcoming exploration programs.
These metals are key to modern electronics and defense applications, positioning Magno as an emerging target for high-tech metal exploration.
“The confirmation of high-grade tin, zinc, and tungsten, and the potential for anomalous indium and gallium at the Magno Project represents a major step forward for GoldHaven Resources. These critical metals are integral to the identification of significant mineralization across the property and the goal of supporting the global clean energy transition and high-tech industries, positioning Magno as a strategically important asset. Our recent compilation work has also revealed impressive historical assays of high-grade silver and gold, further strengthening the project’s polymetallic foundation. With exploration accelerating in both British Columbia and Brazil in the second half of the year, we are well-positioned to advance Magno’s potential and create long-term growth for our shareholders.” – Rob Birmingham, CEO of GoldHaven Resources Corp.
Qualified Person:
The technical and scientific information contained in this news release has been reviewed and approved by Lindsay Bottomer P.Geo. who is a Qualified Person as defined under NI 43-101 and a consultant of the Company.
About GoldHaven Resources Corp.
GoldHaven Resources Corp. is a Canadian junior exploration Company focused on acquiring and exploring highly prospective land packages in North and South America. The Company’s projects include the flagship Magno Project, a district-scale polymetallic property adjacent to the historic Cassiar mining district in British Columbia. The Three Guardsman Project, which exhibits significant potential for copper and gold-skarn mineralization. The Copeçal Gold Project, a drill-ready gold project located in Mato Grosso, Brazil with a 6km strike of anomalous gold in soil samples. Three Critical Mineral projects with extensive tenement packages totalling 123,900 hectares: Bahia South, Bahia North and Iguatu projects located in Brazil.
On Behalf of the Board of Directors
Rob Birmingham, Chief Executive Officer
For further information, please contact:
Rob Birmingham, CEO
www.GoldHavenresources.com
info@GoldHavenresources.com
Office Direct: (604) 629-8254
Neither the CSE nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the CSE- Canadian Securities Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
Cautionary Statements Regarding Forward Looking Information
This news release contains forward-looking statements and forward-looking information (collectively, "forward looking statements") within the meaning of applicable Canadian and U.S. securities legislation, including the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, included herein including, without limitation, exploring skarns with detailed geochemical analysis, looking into verifying historic results, and the timing of future activities of the Company, are forward-looking statements. Although the Company believes that such statements are reasonable, it can give no assurance that such expectations will prove to be correct. Forward-looking statements are typically identified by words such as: "believes", "will", "expects", "anticipates", "intends", "estimates", "plans", "may", "should", "potential", "scheduled", or variations of such words and phrases and similar expressions, which, by their nature, refer to future events or results that may, could, would, might or will occur or be taken or achieved. In making the forward-looking statements in this news release, the Company has applied several material assumptions, including without limitation, that there will be investor interest in future financings, market fundamentals will result in sustained precious metals demand and prices, the receipt of any necessary permits, licenses and regulatory approvals in connection with the future exploration and development of any future projects in a timely manner, the availability of financing on suitable terms for exploration and development of future projects and the Company's ability to comply with environmental, health and safety laws.
The Company cautions investors that any forward-looking statements by the Company are not guarantees of future results or performance, and that actual results may differ materially from those in forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including, operating and technical difficulties in connection with mineral exploration and development activities, actual results of exploration activities, the estimation or realization of mineral reserves and mineral resources, the inability of the Company to obtain the necessary financing required to conduct its business and affairs, as currently contemplated, , the inability of the Company to enter into definitive agreements in respect of possible Letters of Intent, the timing and amount of estimated future production, the costs of production, capital expenditures, the costs and timing of the development of new deposits, requirements for additional capital, future prices of precious metals, changes in general economic conditions, changes in the financial markets and in the demand and market price for commodities, lack of investor interest in future financings, accidents, labour disputes and other risks of the mining industry, delays in obtaining governmental approvals, permits or financing or in the completion of development or construction activities, changes in laws, regulations and policies affecting mining operations, title disputes, the inability of the Company to obtain any necessary permits, consents, approvals or authorizations, including by the Exchange, the timing and possible outcome of any pending litigation, environmental issues and liabilities, and risks related to joint venture operations, and other risks and uncertainties disclosed in the Company's latest interim Management's Discussion and Analysis and filed with certain securities commissions in Canada. All of the Company's Canadian public disclosure filings may be accessed via www.sedarplus.ca and readers are urged to review these materials.
Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. The Company undertakes no obligation to update any of the forward-looking statements. The Company undertakes no obligation to update any of the forward-looking statements in this news release or incorporated by reference herein, except as otherwise required by law.
A photo accompanying this announcement is available at globenewswire.com |





