Blacks are black to protect their cells and DNA from the sun damage. Whites are white to allow enough vitamin D (we get from the sun).
en.wikipedia.org
Real objects never behave as full-ideal black bodies, and instead the emitted radiation at a given frequency is a fraction of what the ideal emission would be. The emissivity of a material specifies how well a real body radiates energy as compared with a black body. This emissivity depends on factors such as temperature, emission angle, and wavelength. However, it is typical in engineering to assume that a surface's spectral emissivity and absorptivity do not depend on wavelength, so that the emissivity is a constant. This is known as the grey body assumption.
Interestingly, this means that every object around you is emitting electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of all values. Every object in the universe has heat, even the emptiness of space, and when the particles that make up an object vibrate on a microscopic level they radiate electromagnetic waves. These wavelengths are predominantly infrared (heat), but there is also a minute amount of visible light like red, yellow, green and blue. So, right now, you and everything around you is emitting visible light. The reason this light cannot be seen is that it has a very low intensity.
When dealing with non-black surfaces, the deviations from ideal black body behavior are determined by both the geometrical structure and the chemical composition, and follow Kirchhoff's Law: emissivity equals absorptivity, so that an object that does not absorb all incident light will also emit less radiation than an ideal black body.
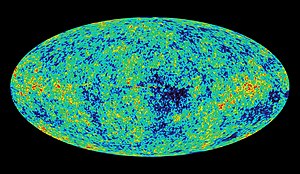
In astronomy, objects such as stars are frequently regarded as black bodies, though this is often a poor approximation. An almost perfect black-body spectrum is exhibited by the cosmic microwave background radiation. Hawking radiation is black-body radiation emitted by black holes.
It is only partly that. It is far from simple.* Blacks did evolve on a savannah, where there is copious sun, but they also lived for millions of years in rainforest where it is hot, but sun can be avoided. The roots of skin area, pores and colouration, can be found in elementary thermodynamics. A perfect absorber is defined as "physics" body which allows light in but does not allow that incident light out at the surface, i.e. no reflection. But that which absorbs, (where it is not a black hole, whose radiation is disallowed at the event horizon), is also conversely a perfect radiator. Heat or light is maximally allowed to emanate from the black body, although capture in the other direction is also perfect. Thus a radiator is necessarily an absorber. That is why we paint them black usually. ( Why would one paint them silver under certain conditions due to "circulation-of-working-fluid timing"..? an engineering exercise.. )
Radiation emitted by a human
Much of a person's energy is radiated away in the form of infrared energy.
Black-body laws can be applied to many things. For example, a great deal of a person's energy is radiated away in the form of electromagnetic radiation - of which, most is infrared.
The net power (energy/second) of energy radiated away is the difference between what someone absorbs from their surroundings and what they radiate themselves:

Plugging in the Stefan-Boltzmann law:

The above equation is applicable to any object which behaves similar to a black body. People have an area of about 2 square meters, and emissivity of nearly 1. They also have a skin temperature of about 32 °C (90 °F, or 305 K). But clothing reduces the surface temperature a few degrees, so in addition to reducing heat loss through conduction, it reduces loss of heat by radiation. So for surface temperature of people we should use 301 K. The temperature of the surrounding environment varies, but for a rough order of magnitude answer, one can use 20 °C (68 °F, or 293 K). Plugging in these values results in a net rate emission of energy for people of about:

In this scenario, people are roughly 100 watt light bulbs, (ed's note: some are only 40 watts) except they emit all infrared and longer wavelength light. The amount of energy in a whole day turns out to be almost 9 million joules, or 2,000 (food) calories. Normal rate of metabolism is typically 100-120 watts, and a person losing more than 160 watts (with extra losses by evaporation, convection and conduction) would feel cold and need to increase activity or cover with clothes. In contrast, during physical activity the metabolism is much higher and since the emission is not large enough, the excess heat is carried by sweating.
Also, applying Wien's Law to humans, one finds that the peak wavelength of light emitted by a person is:

This, presumably, would be the wavelength that infrared goggles would be designed to be most sensitive to. (In fact, 7-14 micrometers is a typical spectral response range for thermal imaging devices designed for human subjects.)
The damaging rays of the sun are not infrared where most heat is generated, but UV. White hominid skin is absorbant of UV allowing D3 manufacture from Cholesterol easily. Thus white skin burns more easily from UV sun rays. Perfectly black people burn too, but they constantly reject the heat that is reflected from the ground, (you get more of that than heat from the sun), and thus can stay cool in any environment. In addition they have 50% more skin area, and more pores per unit area, so their cooling system is more efficient allowing them to endure even high humidity. You would expect however, a greater need for hydration in order to keep that system operating. However given the greater radiation area, and more efficient radiation, the system needs far less evaporation per degree, so the water loss probably remains constant.
When temperatures drop to below freezing, the advantage of heat loss systems turns to a marked disadvantage. Less radiative lighter, coloured skin, far fewer pores, 30% less skin area, matted straight hair covering the largest radiative surface, the head, and tiny invisible cilia skin hairs, make the white skinned person far more able to endure cold. No question that the majority of white skinned race's recent evolution was cold adaptation in the ice covered areas of northern climes. Larger size in general ensued as it was able to endure periods of starvation attendant winter conditions, as game and forage became more scarce. Larger size had less skin area per unit mass as well, another cold advantage. In some areas, an all meat diet became necessary, as fruit and vegetable forage were rare. But the need for D3 in cold foggy overcast climates led the survivor to seek out other D3 sources, which were overwhelmingly fish and cattle. Hence the settling of the coastal areas where fish where abundant around the North and Black seas. Even whites suffer from D3 deficiencies in coastal island areas. In the Mediterranean there is plenty of sun obviating D3 sources from food. Living in Northern Europe causes rickets unless one eats copious Haddock and drinks cow's milk. Survival of the Danes required farming and fishing. The fish intake balanced the increase cholesterol from excess fat and protein intake, but their indoor fires caused epidemic lung cancer. Breeding ages where young with marriage taking place soon after puberty. The women all died in their forties. Societies had to be close knit and tribal to ensure family continuity. Inheritance became an important issue.
The D3 to diet to sun equation is interesting. In America, the sun is so-so. Blacks suffer from 60% more heart disease and cancer than whites.
More than anything, one would think that lack of sun causes early death from disease, meaning mutations cause white skin to arise after migration to the colder climes. The Neandrathal himself may have been hairy but white skinned, as he seems to have been a cold adapted beast. His camp fires were not in his dwellings but scattered about, perhaps for cooking. This cold adaptation may have taken place more than 500,000 years ago. The pre-Iniut Dorset may have been such a people.
In northern Europe, without milk fortification, the children come down with rickets, indicating D3 deficiency among the poor, less fish and meat eating people. In the mediterranean, especially the natural diet island areas like Crete, the sunny less fat and more olive oil and fish eating areas have very low low heart disease. The equation seems to be, rocky soils, high mineral naturally grown vegetables, poorly milled grains, olive oil, walnuts, fish and plenty of sun = less heart disease. What are the greatest commonalities? Near the sea in rocky island areas = High magnesium, plentiful exercise from hill walking, high fish intake with attendant omega 3, not a plentiful diet, whole grains, high fibre, high mineral vegetables, no or few insecticides, copious D3 from fish and sunlight, good lipase and choline from fat in nuts, and good anti-oxidant status from naturally grown vegetables and local forage. The sun and D3 stand out here too, even given the numerous other positive variables. More sun is good for you.
Polar bears are black under UV radiation photography, showing complete absorption of that wavelength. They get their heat from low angle "UV sun". Blue eyes are protective of UV radiation allowing the refraction of that light, hence their blue colour although one would at first think that melanin of the brown eye protects, this is not so.
* In the laboratory, the closest thing to black-body radiation is the radiation from a small hole entrance to a larger cavity. Any light entering the hole would have to reflect off the walls of the cavity multiple times before it escaped and is almost certain to be absorbed by the walls in the process, regardless of what they are made of or the wavelength of the radiation (as long as it is small compared to the hole). The hole, then, is a close approximation of a theoretical black body and, if the cavity is heated, the spectrum of the hole's radiation (i.e., the amount of light emitted from the hole at each wavelength) will be continuous, and will not depend on the material in the cavity (compare with emission spectrum). By a theorem proved by Kirchhoff, this curve depends only on the temperature of the cavity walls. [2]
Calculating this curve was a major challenge in theoretical physics during the late nineteenth century. The problem was finally solved in 1900 by Max Planck as Planck's law of black-body radiation. (Planck (1900)) By making changes to Wien's Radiation Law (not to be confused with Wien's displacement law) consistent with Thermodynamics and Electromagnetism, he found a mathematical formula fitting the experimental data in a satisfactory way. To find a physical interpretation for this formula, Planck had then to assume that the energy of the oscillators in the cavity was quantized (i.e., integral multiples of some quantity). Einstein built on this idea and proposed the quantization of electromagnetic radiation itself in 1905 to explain the photoelectric effect. These theoretical advances eventually resulted in the superseding of classical electromagnetism by quantum electrodynamics. Today, these quanta are called photons and the black body cavity may be thought of as containing a gas of photons. In addition, it led to the development of quantum versions of statistical mechanics, called Fermi-Dirac statistics and Bose-Einstein statistics, each applicable to a different class of particles. See also fermion and boson.
EC<:-} |




